The Importance of Modern Wastewater Systems in Safeguarding Public Health
The Importance of Modern Wastewater Systems in Safeguarding Public Health
Blog Article
Recognizing Wastewater Treatment Processes and Their Ecological Influence
The complexities of wastewater therapy procedures play a crucial role in mitigating ecological challenges related to water pollution. Each stage, from initial to innovative treatments, is made to deal with certain pollutants, inevitably guarding both public wellness and aquatic ecosystems. However, regardless of technical advancements in treatment effectiveness, considerable challenges continue, consisting of the management of recurring toxins and the implications of nutrient overflow. As we discover the intricacies of these procedures, it comes to be important to question how far current methods can advance to fulfill the growing needs of sustainability and environmental preservation.
Introduction of Wastewater Therapy
Exactly how is wastewater changed into a risk-free resource for the environment? Wastewater treatment is a critical procedure developed to remove impurities from made use of water, consequently guarding public wellness and protecting ecological communities. This process begins with the collection of wastewater from residential, commercial, and business resources, which is after that guided to therapy facilities.
At these facilities, numerous physical, chemical, and biological techniques are used to deal with the wastewater. Subsequently, organic therapies, such as activated sludge procedures, utilize bacteria to break down organic issue.
The dealt with effluent can be safely discharged right into natural water bodies or recycled for watering and industrial purposes, advertising resource conservation. In addition, the therapy procedure generates biosolids, which can be repurposed as fertilizers or soil amendments, even more improving sustainability.
Phases of Therapy Procedures
The wastewater treatment process commonly consists of three key stages: preliminary, primary, and second treatment. Each phase offers an unique role in minimizing the toxin load and guaranteeing the effluent meets environmental standards prior to discharge.
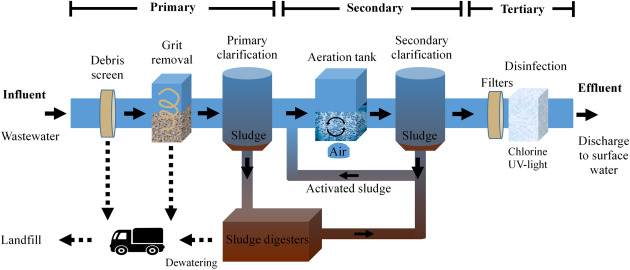
The key treatment stage concentrates on the physical splitting up of suspended solids from the wastewater. Via sedimentation, larger fragments resolve at the end of sedimentation tanks, creating sludge, while lighter products, such as oils and oils, float to the surface and are skimmed. This procedure dramatically lowers the natural and inorganic tons in the wastewater.
Additional treatment is a biological process aimed at more decreasing the concentration of raw material. Various techniques, including triggered sludge systems and trickling filters, use microbes to metabolize natural pollutants. This stage is necessary for accomplishing the essential biochemical oxygen need (BODY) reduction, eventually leading to cleaner effluent ready for discharge or additional treatment. Each stage is critical in securing ecological and public health and wellness.

Advanced Therapy Technologies
Following the second treatment processes, advanced treatment technologies play an essential role in additional boosting the top quality of treated wastewater. These innovations are designed to eliminate residual pollutants that are not efficiently gotten rid of throughout primary and additional treatments, ensuring the effluent satisfies strict governing standards.
Amongst the commonly made use of innovative therapy approaches are membrane layer filtration, reverse osmosis, and advanced oxidation processes. Membrane layer filtering, including microfiltration and ultrafiltration, works in separating great particles, pathogens, and colloids from the water (Wastewater). Reverse osmosis utilizes semi-permeable membrane layers learn the facts here now to eliminate liquified solids, leading to top notch water suitable for various applications
Advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) utilize solid oxidants to degrade organic pollutants, consisting of pharmaceuticals and personal care products that are resistant to standard therapy. These approaches improve the biodegradability of complex compounds, promoting their removal.
One more significant technology is making use of biological nutrient removal processes, which specifically target nitrogen and phosphorus, avoiding eutrophication in getting water bodies. In general, innovative treatment modern technologies are important for attaining higher levels of filtration, advertising water reuse, and safeguarding public wellness while dealing with the challenges related to wastewater management.
Environmental Advantages of Therapy
Many ecological advantages emerge from effective wastewater treatment procedures that add to ecosystem health and wellness and sustainability. Primarily, these processes significantly reduce the release of unsafe pollutants right into natural water bodies, which helps keep aquatic ecosystems. By eliminating contaminants such as heavy metals, nutrients, and pathogens, treated wastewater reduces the risk of waterborne diseases and advertises biodiversity in aquatic environments.
Additionally, wastewater look at this site treatment centers often utilize innovative innovations that enable water recycling and reuse. This method not just conserves fresh water sources yet also reduces the demand on all-natural water materials. Improved nutrient removal from wastewater can additionally stop eutrophication, a procedure that brings about algal blooms and subsequent oxygen depletion in aquatic systems.
Additionally, efficient treatment procedures can minimize greenhouse gas emissions, specifically methane and laughing gas, which are typically launched throughout unattended wastewater disintegration. By recording and utilizing biogas from anaerobic digesters, facilities can transform waste into eco-friendly power, thus adding to a reduction in nonrenewable fuel source dependence.
Challenges and Future Fads
While the environmental benefits of wastewater treatment are clear, numerous challenges linger that impede optimal outcomes in this field. One significant issue is aging facilities, which commonly leads to inadequacies and increased functional expenses - Wastewater. Several treatment plants were developed years ago, and their capacities do not align with contemporary needs, which consist of informative post more stringent regulative criteria and greater quantities of wastewater due to urbanization

Looking ahead, there is a growing emphasis on source recovery and circular economic climate concepts within wastewater therapy. Advancements such as anaerobic food digestion, which can produce biogas, and advanced filtration technologies are acquiring traction. These methods not only boost treatment effectiveness yet additionally advertise sustainability.
Inevitably, resolving these obstacles needs partnership among stakeholders, investment in innovation, and a dedication to continuous study. By welcoming these patterns, the wastewater therapy market can advance to meet the needs of a transforming environment and culture.
Verdict
In verdict, wastewater treatment processes play an essential duty in boosting environmental quality and public wellness. The multi-stage therapy structure, combined with advanced technologies, successfully minimizes air pollution and promotes sustainable water management.
Report this page